
Dipir
Overview :
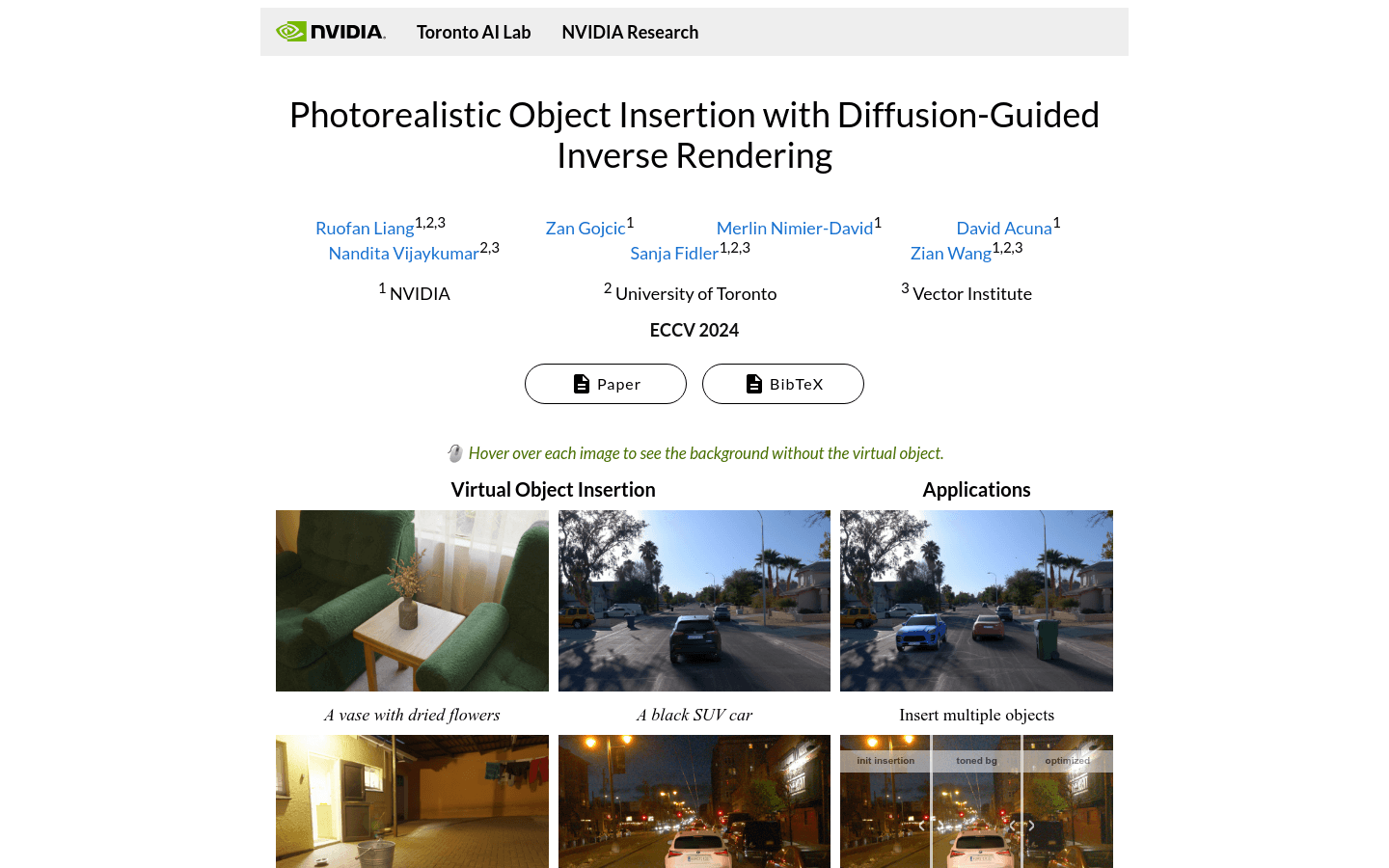
DiPIR is a physics-based method co-developed by the Toronto AI Lab and NVIDIA Research, which recovers scene lighting from a single image, allowing virtual objects to be inserted realistically into both indoor and outdoor scenes. This technology not only optimizes material and tone mapping but also automatically adjusts to different environments to enhance the realism of the images.
Target Users :
Targeted at professionals and researchers in the fields of image synthesis, virtual reality, and augmented reality. DiPIR technology assists them in creating realistic images and videos more efficiently, enhancing work productivity and product quality.
Use Cases
Insert a virtual car into the Waymo outdoor driving scene and optimize the lighting effects.
Use an indoor HDRI panorama as a background to insert virtual decor and optimize material and tone mapping.
Animate virtual objects or move them within a dynamic scene to create more realistic visual effects.
Features
Recover scene lighting from a single image.
Achieve realistic synthesis of virtual objects in indoor and outdoor scenes.
Automatic optimization of material and tone mapping.
Support for the synthesis of virtual objects in single frames or videos.
Guide the physics-based inverse rendering process using personalized diffusion models.
Evaluate with different background images, such as Waymo outdoor driving scenes and indoor HDRI panoramas.
Improve the accuracy of virtual object insertion through the diffusion-guided lighting optimization process.
How to Use
1. Prepare a target background image, which can be an indoor or outdoor scene.
2. Select or create a virtual object model and place it in the scene.
3. Use the DiPIR model to recover the scene lighting from the background image.
4. Adjust the material and tone mapping parameters of the virtual object based on the recovered lighting effects.
5. Utilize DiPIR's diffusion-guided inverse rendering technique to optimize the compositing effects of the virtual object in the scene.
6. Evaluate the composite result and make further adjustments and optimizations as needed.
7. Once composition is complete, export the final image or video.
Featured AI Tools
Chinese Picks

Capcut Dreamina
CapCut Dreamina is an AIGC tool under Douyin. Users can generate creative images based on text content, supporting image resizing, aspect ratio adjustment, and template type selection. It will be used for content creation in Douyin's text or short videos in the future to enrich Douyin's AI creation content library.
AI image generation
9.0M

Outfit Anyone
Outfit Anyone is an ultra-high quality virtual try-on product that allows users to try different fashion styles without physically trying on clothes. Using a two-stream conditional diffusion model, Outfit Anyone can flexibly handle clothing deformation, generating more realistic results. It boasts extensibility, allowing adjustments for poses and body shapes, making it suitable for images ranging from anime characters to real people. Outfit Anyone's performance across various scenarios highlights its practicality and readiness for real-world applications.
AI image generation
5.3M














